We explain what the Neolithic revolution is, how it originated and its main inventions. Also, their characteristics, religion and more.
What is the Neolithic Revolution?
The Neolithic revolution was a crucial change in the ways of life of humanity , in which one goes from a nomadic lifestyle to a sedentary one, which also entails an economic transformation, from a collecting economy to an economy producer.
Although it is known as "revolution", historians insist that it was a rather gradual change , which occurred, according to Gordon Childe (1941), the most accepted theory so far, in the eighth millennium BC, due to a climate crisis at the beginning of the Holocene. On the basis of its importance for the history of mankind, he claimed the term "revolution" for himself.
It stretches from the Paleolithic period , when stones were still carved, to the Neolithic period , when the stones were polished, all for the purpose of making tools and weapons . It is part of what has been characterized as the “ Stone Age ”.
Next, and as a summary of the Neolithic revolution, we present the most important characteristics.
Characteristics of the Neolithic revolution :
Source
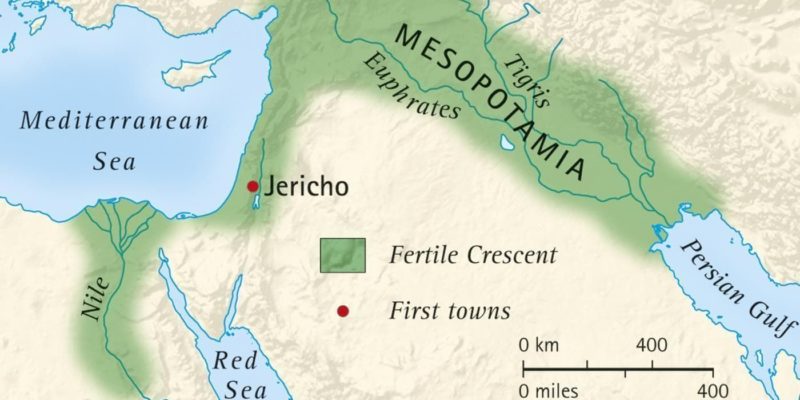
According to Gordon Childe, it occurred in the “Fertile Crescent” , which covers the Egyptian area from the Nile Valley ( Africa ) to Mesopotamia , between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers ( Asia ). The cause would have been a climate change, which produced a dry land and man had to plant and reproduce nearby animals . Due to the influx of the Tigris and the Euphrates, livestock and agriculture became possible. This would be the center from which the Neolithic would spread.
According to Braidwood (1971), climate change was not the main cause since it had already happened before . Nor does he consider that Mesopotamia was the center. According to him, what most explains the transformation has to do with the degree of advancement that humanity had then.
-
farming
Domestication of animals
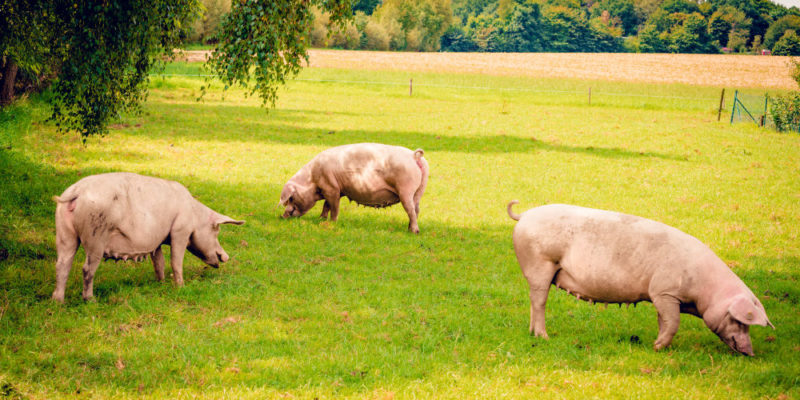

The first animal to enter the human habitat was the dog . The domestication of sheep, cattle and goats constitute a fundamental pillar of production today. The domestication of the horse occurred at that time , in the Central Asian area, along with that of the camelids, which occurred in different sectors.
Among the mammals that were selected for livestock, the pig occupied a main place . Poultry and raptors were used, particularly ducks and chickens. There is information about the use of insects , for example in beekeeping -bees- and in sericulture -silk worms-.
-
Invention of textiles
Microlitization
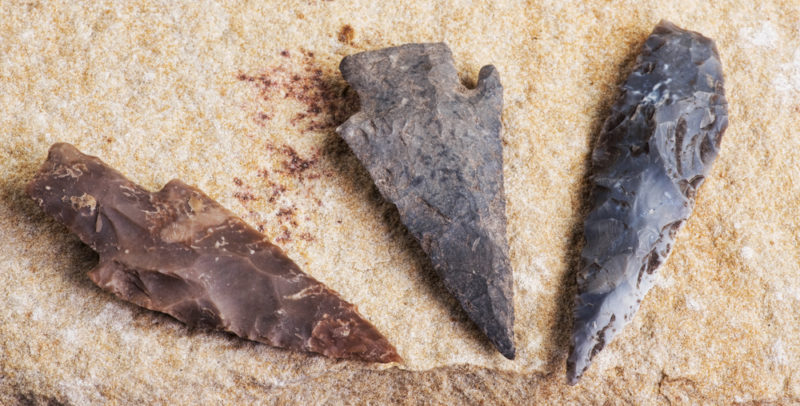

This is the name given to the reduction of lithic elements (stonework) , which allows greater flexibility in their use and standardized production to create more tools, for example, arrowheads. This tendency to microlitization is already recorded in the end of the Paleolithic, but it is intense from the Neolithic revolution.
-
Creation of ceramics
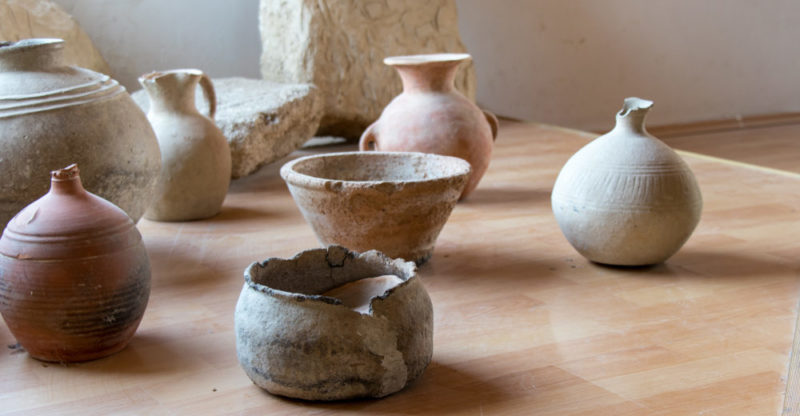 It happens around the VII millennium BC, in Anatolia . What was called "empty space" appears, for the containment of food and the kitchen on fire . Still, some Near Eastern cultures were found to already use pottery. However, it is worth highlighting the extensive and varied use that was given to ceramics during this period, in which the construction of agricultural instruments is more important than hunting.
It happens around the VII millennium BC, in Anatolia . What was called "empty space" appears, for the containment of food and the kitchen on fire . Still, some Near Eastern cultures were found to already use pottery. However, it is worth highlighting the extensive and varied use that was given to ceramics during this period, in which the construction of agricultural instruments is more important than hunting.
Migration
At this point, it should be noted that livestock, through transhumance, allows communication between distant men -and villages.
-
Division of labour
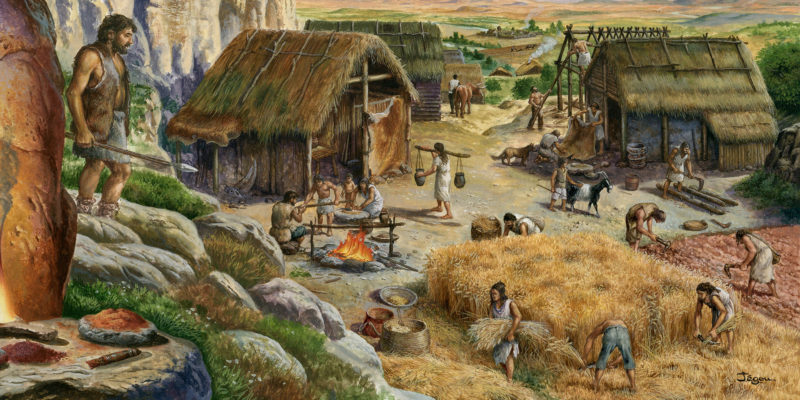 In the Neolithic there was a demographic increase with respect to the Paleolithic, thus society was divided between those who plowed the land, those who harvested, those who polished the stones , the gatherers, those who work the ceramics and used the looms -mainly women- , those who built the houses and those who looked after the livestock. It is necessary to mention the entry into the scene of the surplus. From its appearance, it is possible to exchange goods . This first type of trade is called barter.
In the Neolithic there was a demographic increase with respect to the Paleolithic, thus society was divided between those who plowed the land, those who harvested, those who polished the stones , the gatherers, those who work the ceramics and used the looms -mainly women- , those who built the houses and those who looked after the livestock. It is necessary to mention the entry into the scene of the surplus. From its appearance, it is possible to exchange goods . This first type of trade is called barter.
Animistic religion
Due to the practice of farmers, a special relationship with the land is lived . She represents the "Mother-Goddess", fertility, the cycle of life and death.
-
Emergence of private property
The above content published at Collaborative Research Group is for informational and educational purposes only and has been developed by referring reliable sources and recommendations from technology experts. We do not have any contact with official entities nor do we intend to replace the information that they emit.
MA student of the TransAtlantic Masters program at UNC-Chapel Hill. Political Science with a focus on European Studies. Expressed ideas are open to revision. He not only covers Technical articles but also has skills in the fields of SEO, graphics, web development and coding. .
Leave a reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Recent post

Sport: What Is It, Types, Risks, Features, Characteristics and Examples

Dogs: Emergence, Features, Characteristics, Feeding and Breeds

Story: Definition, Elements, Structure, Features and Characteristics

