We explain what lysosomes are and what their main characteristics are. Also, what are its functions and more.
What are lysosomes?
Lysosomes are membranous structures found inside animal cells that contain enzymes . These enzymes are responsible for digesting substances that are inside and outside the cell.
It could be said that lysosomes function as a stomach for cells , because they are responsible for the elimination and recycling of waste substances.
The cell reuses the substances resulting from the work of lysosomes as fuel or to form new molecules . That is, lysosomes also influence cell growth and survival.
Discovery of lysosomes
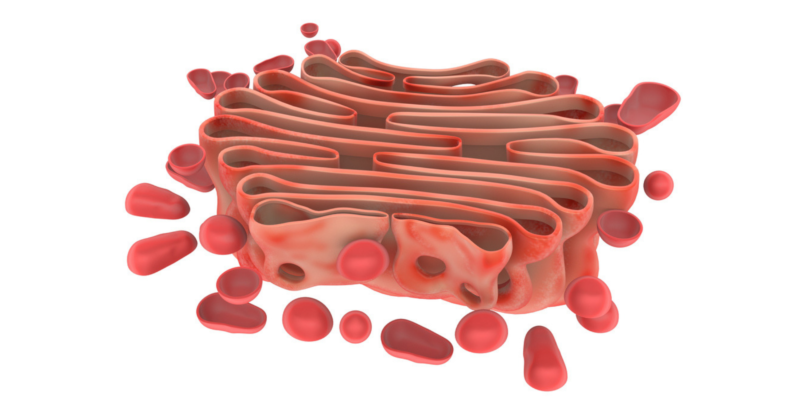
In 1974 the English biochemist Christian de Duve discovered organelles (parts of the cell that perform the function of an organ) called "lysosomes". Lysosomes are composed of various enzymes that contribute to the digestion of particles (which come from outside or inside the cell) and to the self-disintegration of the cell when it cannot be recovered.
In addition, he discovered that lysosomes play an essential role in defending the body against bacteria . This was a very important contribution for medicine and for the treatment of hereditary diseases caused by the deficiency of lysosomal enzymes.
Characteristics of lysosomes
Lysosomes are made up of different types of enzymes.
Lysosomes have a very acidic composition (with a pH of 5.0), so they are surrounded by a membrane to protect them from contact with the rest of the cell. They are composed of different types of enzymes that are responsible for digesting different types of substances. Some of those enzymes are:
- The lipases. They are responsible for digesting liquid substances .
- Glucosidases. They are responsible for breaking down and digesting carbohydrates .
- Proteases. They are responsible for digesting proteins .
- Nucleases. They are responsible for degrading nucleic acids.
See also: Microorganisms
Functions of lysosomes
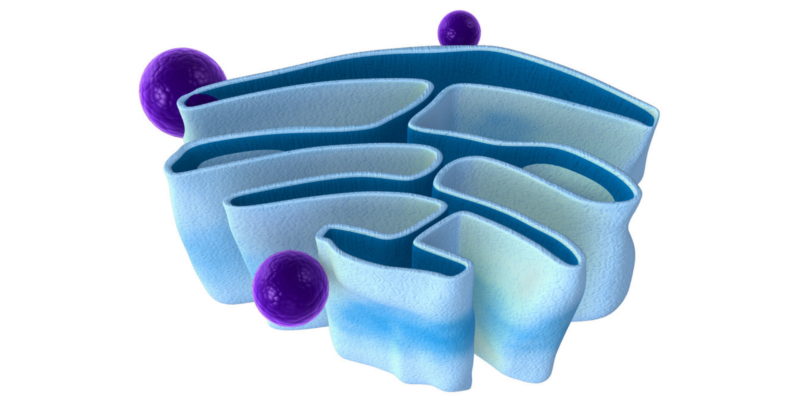 Lysosomes are an elemental part of the cell and fulfill various functions, such as:
Lysosomes are an elemental part of the cell and fulfill various functions, such as:
- They are in charge of eliminating or recycling cellular debris and waste.
- They store digestive enzymes that provide the necessary nutrients for the cell.
- They destroy invading viruses and bacteria .
- They participate in the process of self-destruction if a cell is damaged and cannot be repaired (a process called "autophagy").
More recent research shows that the functions of lysosomes go beyond the elimination or recycling of waste. They can also integrate and transmit nutritional information . That is, they have the ability to perceive the nutritional status of the cell and, consequently, of the entire organism.
When the individual is hungry, the lysosomes tell the cell that it is necessary to manufacture more of these organelles for their enzymes to mobilize fat stores as fuel for energy.
The above content published at Collaborative Research Group is for informational and educational purposes only and has been developed by referring reliable sources and recommendations from technology experts. We do not have any contact with official entities nor do we intend to replace the information that they emit.
Luke is passionate about fostering student involvement and connection. He studied psychology for his major and likes learning about the past. Luke aims to specialize in artificial intelligence and cybersecurity. .
Leave a reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Recent post

Sport: What Is It, Types, Risks, Features, Characteristics and Examples

Dogs: Emergence, Features, Characteristics, Feeding and Breeds

Story: Definition, Elements, Structure, Features and Characteristics

