We explain what plate tectonics are and why they are important in the formation of relief. In addition, its characteristics and classification.
what are tectonic plates?
The tectonic plates are the different rigid and uniform portions into which the lithosphere can be divided, that is, the earth's crust in its outermost portion, and which are suspended over the upper mantle of the Earth (or asthenosphere), whose semi-liquid allows them to move or move.
The movements of these plates of the lithosphere obey what is described by plate tectonics, a scientific theory that originated in the middle of the 20th century and which allows explaining, through the interactions between said plates, the various terrestrial and relief phenomena, such as the formation of the mountains, the earthquakes, and volcanoes.
According to this theory, the different existing tectonic plates move over the mantle like a kind of raft, brushing, colliding, and pushing each other, in a field of geological stresses.
The greatest evidence in this regard seems to be that the current shape of the continents allows us to suppose that they fit together millions of years ago, like pieces of a puzzle, constituting a single supercontinent called Pangea. The sustained tectonic movement would have separated the continents down to their current distribution.
Tectonic plate shape

Tectonic plates are rigid, concrete and solid, but different from each other in terms of their shape, which is irregular, and their thickness, which is variable. They do not coincide with the shape of the continents as we represent them on a map, since the same content can be only the visible part (not covered by water) of one or even several neighboring tectonic plates.
Number of tectonic plates
There are numerous known tectonic plates, of which some 15 larger (main) plates and about 42 lower (secondary) plates stand out.
The geological activity of tectonic plates
The processes of the depths of the Earth are a consequence of the dynamism of the tectonic plates. Since the heart of our planet is liquid and consists of various molten metals, the tectonic plates constitute the segments of the outer and coldest, therefore more solid, a layer of the planet. When that underground magma erupts (as in volcanoes), new chemical elements are thrown to the surface.
Main tectonic plates

The main known tectonic plates are fifteen:
- African plate. Located around the African continent.
- Antarctic plate. Located around the Antarctic continent and the South Pole.
- Arabic plate. Located around the Middle East.
- A plate of Coconuts. Located on the Central American coast of the Pacific Ocean.
- Nazca plate. Located in the Pacific Ocean, next to the Peruvian, Chilean, and Ecuadorian coastline.
- Caribbean plate. Located throughout the Caribbean Sea region, north of South America.
- Pacific Plate. Located in the portion of the middle Pacific Ocean, which borders the Nazca, Juan de Fuca, Cocos, Indo-Australian, Filipino, and North American plates.
- Eurasian plate. Located around the entire European continent and most of Asia.
- Philippine license plate. Located in the Southeast Asian territory of the Philippine Islands.
- Indian plate. Located in the territory of India and its surroundings.
- Australian or Indo-Australian license plate. Located around much of Oceania and its adjacent seas.
- Juan de Fuca plaque. Located on the west coast of the United States.
- North American plate. Located around the North American continent, Greenland, Iceland, and part of eastern Russia.
- Scotia plate. Located south of the South American continent and bordering Antarctica.
- South American plate. It includes the territory of the South American continent and its portion of the adjacent Atlantic Ocean.
Types of tectonic plates
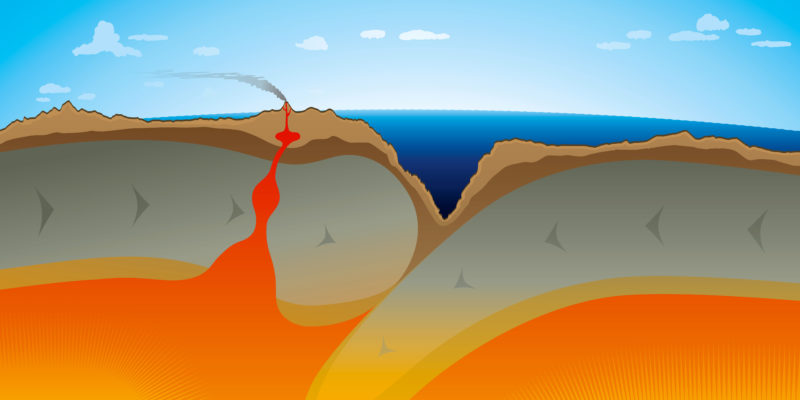
There are two types of a tectonic plate, depending on the crust of which it is part:
- Ocean plates. Those covered almost entirely (except for the eventual appearance of islands, that is, intraplate volcanic buildings) by oceanic water, and their composition is predominantly metallic: iron and magnesium.
- Mixed plates. Those that combine oceanic and continental crust, so are very varied in their composition.
Plate tectonic boundaries
The limits between one tectonic plate and another are given in three possible ways:
- Divergent limits. The plates move away from each other, due to the pressure of the underground magma that emerges, creating a new portion of crust as it cools.
- Convergent limits. Tectonic plates approach the point of collision, being able to generate subduction zones, that is to say, in which one plate penetrates the mantle below the other; or wrinkle the surface crust thus giving rise to mountain ranges and mountains.
- Friction limits. In these limits, neither crust is created nor destroyed, but it is kept in parallel movement generating a lot of friction, and therefore they are regular seismic zones.
Tectonic accidents
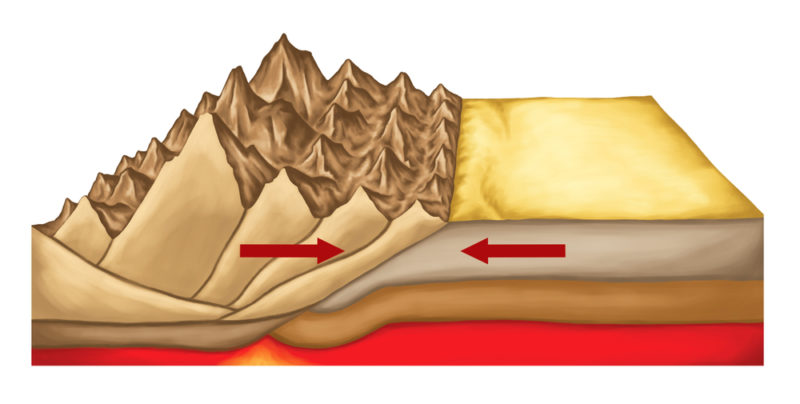
Three types of accidents are known as a consequence of tectonic dynamics:
- Volcanism The emergence of volcanoes, continental or underwater, in which the magma rising from the subsoil is released and new crust is generated when it cools.
- Orogenesis. Formation of mountains and ranges. This can occur both in the cases of collision and wrinkling of plates, as well as in the subduction of the same. In the first case, the volcanism is low and the seismicity is intense; in the second, on the other hand, there is little seismicity and a lot of volcanism.
- Seismicity The appearance of earthquakes and tremors is a consequence of friction between tectonic plates.
The particularity of tectonic plates
Planet Earth is the only planet in the solar system that shows tectonic activity that we know of. Although Mars, Venus, and some satellites of Saturn present indications of having ever had it.
Convection currents
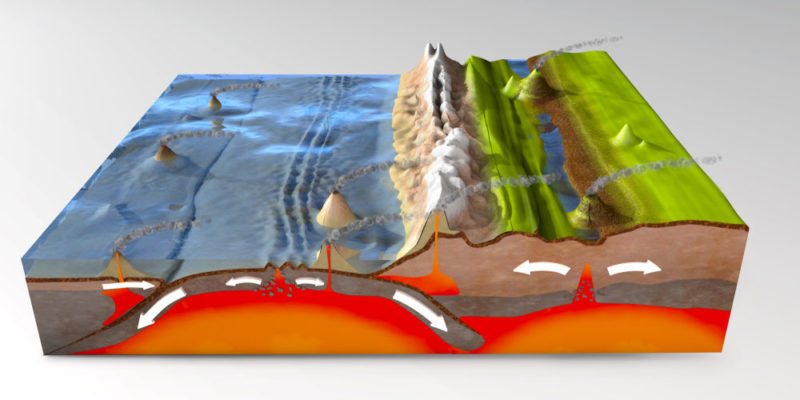
This is the name given to the currents that move underground material, pushing the hotter and less dense material out (due to the high temperatures inside the Earth). This material presses on the lithosphere and gradually cools, descending back into the deep mantle; but this cycle generates pressure that mobilizes the tectonic plates between them.
Plate tectonic density
The continental plates, contrary to what it might seem, are lighter in their composition than the oceanic ones, which present denser and heavier elements. This explains the difference in movement between one and the other, and the distribution of tectonic activity throughout the planet.
The above content published at Collaborative Research Group is for informational and educational purposes only and has been developed by referring to reliable sources and recommendations from technology experts. We do not have any contact with official entities nor do we intend to replace the information that they emit.
Veronica is a culture reporter at Collaborative Research Group, where she writes about food, fitness, weird stuff on the internet, and, well, just about anything else. She has also covered technology news and has a penchant for smartphone stories. .
Leave a reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Recent post

Sport: What Is It, Types, Risks, Features, Characteristics and Examples

Dogs: Emergence, Features, Characteristics, Feeding and Breeds

Story: Definition, Elements, Structure, Features and Characteristics

