We explain what the plant cell is, what its structure and its elements are like. Also, what are its features and functions.
What is the plant cell?
The cell is the minimum unit of life. All living things are made up of cells. The plant cell is a type of eukaryotic cell , that is, it has a nucleus where the genetic material is found and is delimited by a nuclear membrane.
Plant cells are multicellular organisms . There is no relationship between plant size and cell size. A larger plant has a greater number of cells.
Plant cells have some characteristics in common, such as the cell wall, the plastids, and the central vacuole . However, they also specialize and differentiate from each other, depending on the role they fulfill within the plant.
Characteristics and features of the plant cell :
Cell membrane and cell wall
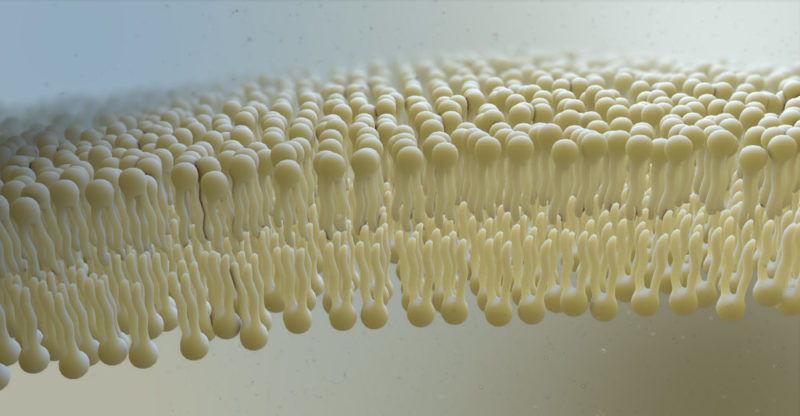
All cells, both plant and animal, are surrounded by a membrane that delimits them , also called the plasma membrane.
It is a double layer of lipids (phospholipids and glycolipids) and proteins . This membrane is porous, that is, it allows the exchange of water and other substances with other cells.
Plant cells are characterized by having, in addition to the cell membrane, a second envelope called the cell wall . Depending on the type of plant cell, the cell wall is stiffer or more flexible.
-
Nucleus and nuclear membrane
The nucleus is surrounded by a porous membrane that allows the exchange of specific molecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm .
Cytoplasm
It is made up of the cytosol, also called hyaloplasm , which is an aqueous solution where all the cell's organelles are found, including chloroplasts.
It is everything that surrounds the nucleus of the cell and is limited by the cell wall and the cell membrane .
-
Chloroplasts and other plasts
Chloroplasts are the organelles that distinguish plants from other organisms . They are responsible for photosynthesis.
They are covered with two concentric membranes , within which are vesicles called thylakoids. Thylakoids capture light for photosynthesis and photophosphorylation. In their membranes are the photosynthetic pigments: chlorophyll, carotenoids and xanthophylls.
In addition to chloroplasts, other plasts such as leukoplasts and chromoplasts are found in plant cells .
Organize them
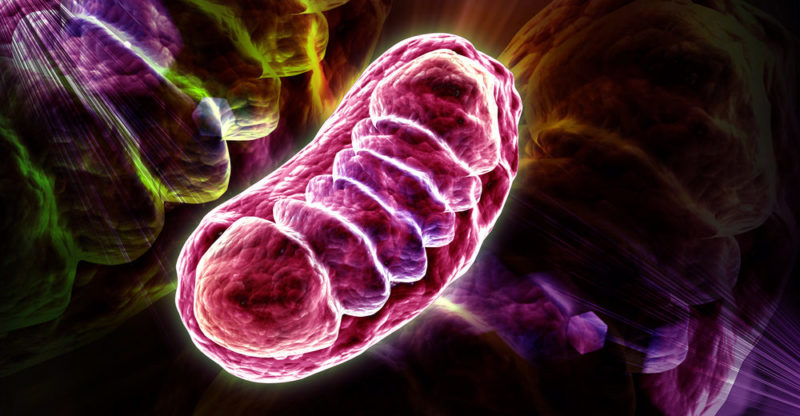
In addition to chloroplasts, which are exclusive to plant cells, there are other organelles in the plant cytoplasm, which can also be observed in the animal cell:
- Mitochondria. They synthesize ATP from glucose in the process of photophosphorylation.
- Endoplasmic reticulum. It is found throughout the cytoplasm. It is a network of membranes that form bags and tubes connected to each other.
- Ribosomes . They are complexes of proteins and RNA that are also found in the cytoplasm but also in the mitochondria and chloroplasts. They are responsible for producing proteins.
- Golgi apparatus . It modifies the vesicles of the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
- Central vacuole. It is a volume of water enclosed in a membrane. Although animal cells also have vacuoles, a single large vacuole is found in the plant cell.
- Vesicles They are responsible for storing, transporting or digesting products and cellular waste.
-
Parenchyma cells

Among the cells of the parenchyma are epithelial cells . They also form tubers, such as the potato (potato), where they fulfill storage functions.
Collenchyma cells
Collenchyma is the supporting tissue in herbaceous plants and older plants in young stages . The function of these cells is to offer flexibility to the stems.
That is, they offer a plastic support . Unlike sclerotic cells, these cells become mature. Its cell wall is composed mainly of pectin and hemicellulose.
They are elongated cells, which favors their flexibility and also collaborates with the length of the plant . In addition to being in stems, they also make up the veins of the leaves.
-
Sclerotic cells
 The sclerenchyma of plants is what gives them their mechanical support and is made up of tough cells . These cells have two cell walls, which gives them greater resistance.
The sclerenchyma of plants is what gives them their mechanical support and is made up of tough cells . These cells have two cell walls, which gives them greater resistance.However, the secondary cell wall is also impermeable: they cannot receive water from other cells and they die quickly . When they die and their cytoplasm is empty, they continue to fulfill functions for the plant, since they retain their hardness.
Among its functions is to give resistance to leaves and stems and, in some cases, they are also defense against herbivorous animals and insect larvae . Unlike collenchymal cells, they offer rigid support.
Xylem cells
Its function is to conduct the water throughout the plant . They are one of the oldest types of cells since they appeared more than 400 million years ago.
Angiosperm plants (flowering plants), in addition to having xylem cells , have cells that form vessels in the xylem .
-
Phloem cells
 These cells exist in higher plants. They are responsible for transporting sucrose to various places in the plant. Sucrose moves from one cell to the other through osmosis.
These cells exist in higher plants. They are responsible for transporting sucrose to various places in the plant. Sucrose moves from one cell to the other through osmosis.Phloem cells can be:
- Cells of the sieve tube. They do not have a cell nucleus or ribosomes.
- Complementary cells. They have a nucleus and regulate the metabolism of the cells of the sieve tube. They are responsible for providing sugars (including sucrose) to the phloem.
The above content published at Collaborative Research Group is for informational and educational purposes only and has been developed by referring reliable sources and recommendations from experts. We do not have any contact with official entities nor do we intend to replace the information that they emit.
Abubakr Conner brings a diverse skill set to our team, and covers everything from analysis to the culture of food and drink. He Believes: "Education is the most powerful weapon that exists to change the world." .
Leave a reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Recent post

Sport: What Is It, Types, Risks, Features, Characteristics and Examples

Dogs: Emergence, Features, Characteristics, Feeding and Breeds

Story: Definition, Elements, Structure, Features and Characteristics

