We explain what art is, the history of its origin and the types that exist. Also, what are its general characteristics and importance.
What is the art?
Art or arts is called a set of human activities of a creative, communicative and subjective nature , which pursue an aesthetic purpose, that is: they try to move, produce beauty, awaken feelings or reflections, all through the manipulation of materials of diverse nature.
One of the most important features of art is its ability to last over time , allowing later generations (or even later cultures ) to know something about the history , beliefs, language and/or sensibilities of the society and time. in which it was created. In this way, art is also a historical element.
Those who engage in the creation of art are known as artists . There are also those who specialize in the interpretation, classification and study of art , called art critics .
Art Concept

There is no single and definitive concept of art, since the question about what art is is part of the explorations that art itself poses. In any case, art is an important part of human culture. It is a concept that changes over time , allowing the inclusion of new forms, content and techniques to what is known at the time.
Currently, the concept of art comes from a generalization of what was called "Fine Arts" in the eighteenth century , to distinguish them from crafts and popular manifestations. This concept, already in disuse, included literature, sculpture, painting, music, dance and architecture. In the 20th century , cinema, photography and comics were incorporated.
Origin of Art
The first artistic manifestations of the human being date from prehistory , when the first tribes of Homo sapiens (and perhaps of Homo neanderthaliensis ) decorated the interior of the caves in which they lived with mixtures of pigments and animal fat.
Those first forms of cave art were drawings of totem animals, hunting scenes or impressions of their own hands , who knows if for narrative, shamanic or ritual purposes. Many of those paintings are preserved to this day.
However, the concept of art itself did not always exist , but rather emerged in classical antiquity , especially in the great cultures, such as the Chinese or the Greco -Roman . The latter was also the first to produce theoretical or critical texts regarding art, such as Aristotle's Poetics , for example, founder of literary criticism.
Plutarch's studies also come from the Greco-Roman culture , who distinguished for the first time between "useful arts" (such as current sciences ) and "pleasant arts" (such as current arts).
History of Art

In ancient times, especially Greco-Roman, the arts were associated with divine influence . The ancient Greeks had specific muses for each form of art, to whom they attributed the necessary inspiration for their exercise.
During the Middle Ages , in the West , the arts began their separation from what was called artificium , that is, "mechanical" or "vulgar" arts , distinguishing between what was later called crafts ( ceramics , goldsmithing, etc.) and what which was called “liberal” arts, which were supposedly the arts of the spirit. During this period the arts were at the service of Christianity .
This concept was accentuated after the sixteenth century , after the artistic and philosophical outbreak of the European Renaissance . Since then, it began to be considered that the artistic profession (especially painting, architecture and sculpture) required something more than simply craft and skill: it required a certain artistic genius. These were then called “design” arts.
Thus , in the 18th century, the concept of “Fine Arts” arose . The great diversification and liberalization of the arts in the 19th and 20th centuries resulted in the consideration of art as the pinnacle of humanity's expressive genius, a more or less refined way of recording our passage through the world.
Types of Art

There are many ways to classify art, such as periods, cultures of origin or, the main one, according to the nature of its representation. Thus, we can talk about:
- Decorative arts. Combination of art and craftsmanship, aimed at producing beautiful as well as functional objects, thus combining the industrial and artisanal worlds. They are also known as applied arts or industrial arts.
- Plastic arts. Those that use materials that the artist can modify, alter or combine to produce a work. This term is deprecated in favor of the broader "visual arts." Traditionally, "plastic" refers to painting, drawing, sculpture, engraving and other forms of ceramics and goldsmithing.
- performing arts Those that need to be performed on a formal stage (a theater, for example) or informal (a square), and that have an audience that watches the show. It traditionally refers to dance, theater , music, and film.
- literary arts. Literature is the art form that uses language and writing to produce aesthetic works, whether of a rhythmic and descriptive type ( poetry ), narrative ( novel , short story ) or theatrical texts (dramaturgy).
Artistic Disciplines

Traditionally, nine artistic disciplines are recognized, also called "Fine Arts", which are:
- Painting . Visual artistic expression, which uses colors and shapes to produce still works on a two-dimensional canvas.
- Sculpture . The construction of three-dimensional objects endowed with shape, color and volume, and even in some cases penetrability or interactivity, to provide the viewer with an aesthetic experience.
- literature . Artistic expression through the use of the word and its written resources, to produce legible and interpretable textual bodies.
- Music . Through the execution of various types of instruments (string, wind, percussion, etc.), music offers the viewer an experience of harmony, melody and rhythm, in which the human voice may or may not intervene.
- Architecture . It is about the construction of spaces and buildings that can be inhabited and that also provide their inhabitants with a sense of beauty or that transmit a specific aesthetic message.
- Dance . Those artistic expressions that use the human body on stage, accompanying it with music or other rhythmic forms to express an aesthetic content.
- Cinema . An art form that consists of the sequential montage of images and sounds that can then be projected and reproduced on a stage, to give the public a sense of movement and an aesthetic audiovisual experience.
- Photography . Forerunner of cinema, it consists of capturing light on photosensitive surfaces or devices, capturing the image of the surrounding reality and then reproducing it motionlessly.
- Sequential art. The so-called cartoon , comic or vignettes, is a form of narration that combines text and image with elements of graphic design, to produce an aesthetic experience.
Art Function
Art, said Oscar Wilde, is profoundly useless. That is, it does not fulfill explicit functions nor is it applicable to anything . But at the same time it can fulfill involuntary functions: document of an era, personal testimony, decoration or embellishment of a space or a city , or a vehicle for the transmission of cultural , ethical or spiritual values.
Artworks
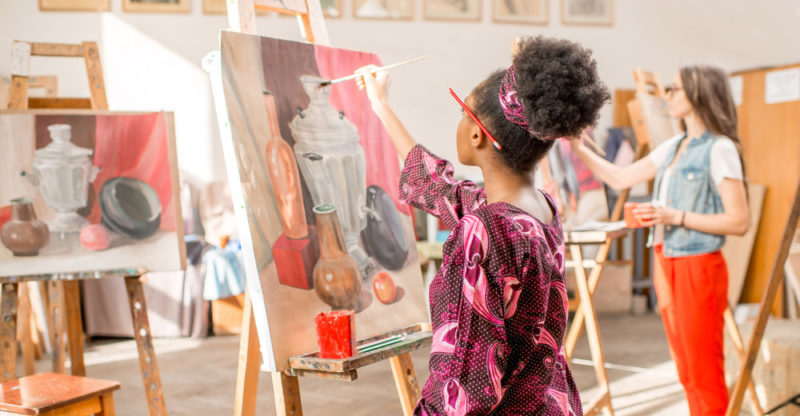 Art is an abstract, intangible concept . But the works in which he expresses himself are not, regardless of their genre and discipline. Some works of art are more concrete, such as a painting, a sculpture or a building, while others are intangible and require a written or audiovisual support, such as a symphony, a novel or a theatrical or dance performance.
Art is an abstract, intangible concept . But the works in which he expresses himself are not, regardless of their genre and discipline. Some works of art are more concrete, such as a painting, a sculpture or a building, while others are intangible and require a written or audiovisual support, such as a symphony, a novel or a theatrical or dance performance.In any case, works of art endure over time and acquire more and more possible interpretations as generations know them, version them and spread them.
Importance of Art
Art is one of the most important and lasting manifestations of what is human. Thanks to art we can reflect on our own condition , our sensitivities, or we can communicate our anxieties, shape our fears, in short, carry out a whole spiritual task that is part of who we are as a species.
Artistic Restoration
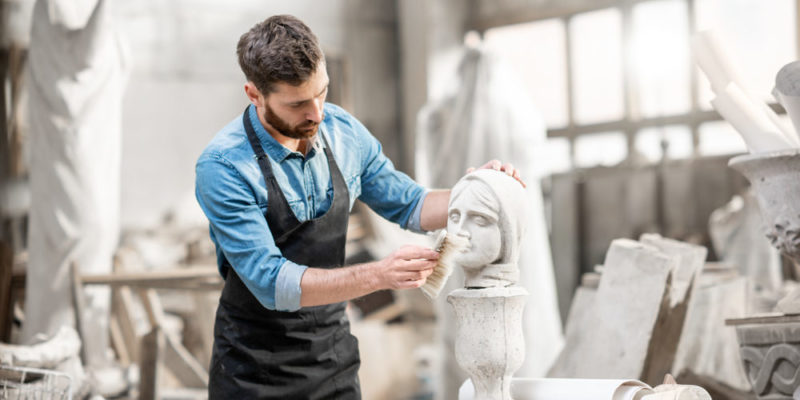
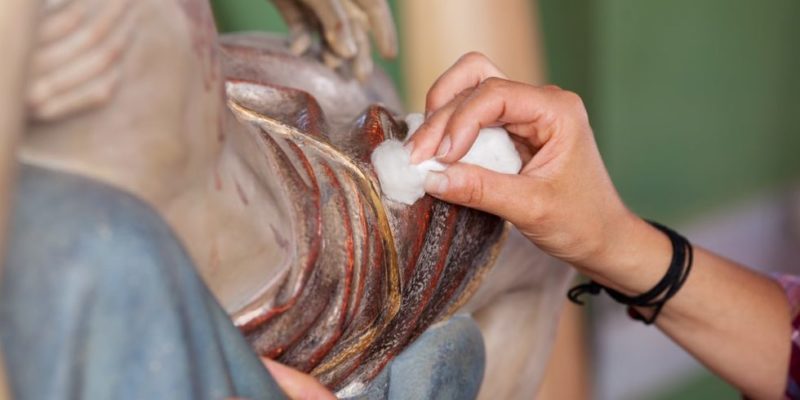 Works of art lose some of their perfection over time as the materials age. For this reason, there is a need for restorers: professionals who, imitating the techniques with which the work was originally done, propose to restore or replicate it.
Works of art lose some of their perfection over time as the materials age. For this reason, there is a need for restorers: professionals who, imitating the techniques with which the work was originally done, propose to restore or replicate it.In this way , it is guaranteed that the work can continue to be exhibited and is preserved for later generations. It is usual for each museum to have its own team of restorers.
Examples of Art
Examples of art abound in everyday life. The music that the orchestra plays during a performance, the paintings and sculptures that a museum exhibits, the poems that abound in books or the beautiful architectural spaces that we can visit, are all examples of the artistic capacity of the human being .The above content published at Collaborative Research Group is for informational and educational purposes only and has been developed by referring to reliable sources and recommendations from experts. We do not have any contact with official entities nor do we intend to replace the information that they emit.
Cultural journalist with great interest in education and technological innovation in the classroom. The future passes through technology and it is already here. .
Leave a reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Recent post

Sport: What Is It, Types, Risks, Features, Characteristics and Examples

Dogs: Emergence, Features, Characteristics, Feeding and Breeds

Story: Definition, Elements, Structure, Features and Characteristics

