We explain what the cerebellum is, what its anatomy is like and its main functions. Also, what are its characteristics, diseases and more.
What is the cerebellum?
The cerebellum is a structure of the central nervous system . It is the largest part of the brain after the brain . It is located in the back and lower part of the skull.
The main function of the cerebellum is to integrate motor and sensory pathways. In short, it receives information and orders from the cerebral cortex and connects them with the locomotor system . It is also responsible for some processes of memory , language , attention, learning, among other functions. However, the cerebellum is not responsible for any of the functions of the olfactory system.
The cerebellum, in addition, is responsible for physiological tremor . It is for this reason that when faced with an injury in this part of the brain, paralysis does not occur, but it can generate disorders in motor performance, balance or body posture.
Appearance of the cerebellum
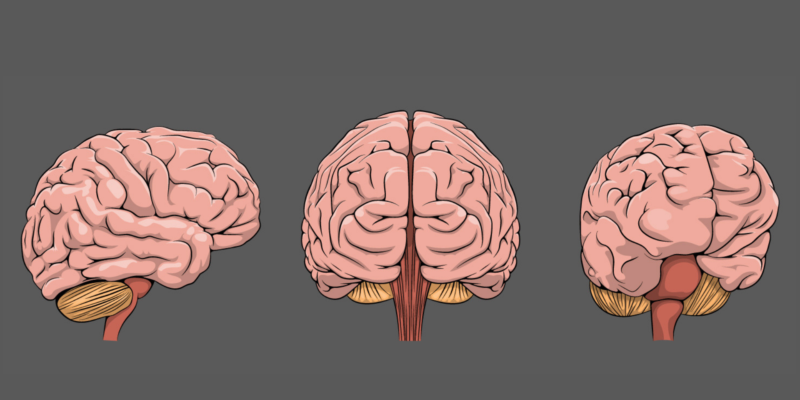
It is ovoid in shape, weighs between 150 and 180 gr . The cerebellum of men weighs 9 grams more than that of women. They are 8 cm x 5 cm x 5 cm in size. The entire cerebellum is covered by a cerebrospinal fluid . It has 3 faces: anterior, superior and inferior:
- The anterior surface connects the medulla oblongata with the annular pons.
- The upper face is shaped like a roof and connects with a part called the tentorium cerebellum.
- The underside is supported by the dura mater. It connects with the occipital fossa of the skull (cerebellar fossae).
Cerebellum anatomy
It is made up of two hemispheres in the center of which there is a small cavity called Vermis . This narrow structure is shaped like a worm. There the unconscious nervous pathways lodge or end.
Main function of the cerebellum
As we have mentioned previously, its main function lies in coordinating the sensory and motor pathways . That is, it makes the muscles react to sensory stimuli. It is the cerebellum that reacts or responds quickly to an external danger signal and sends the signal to the brain to react quickly and the reaction occurs.
Neurons
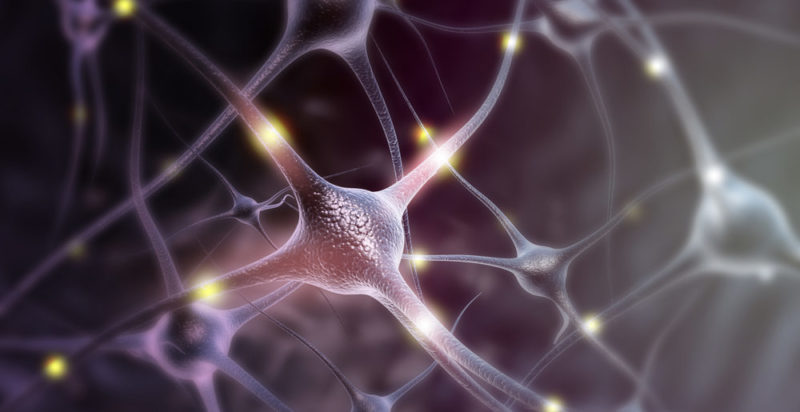
Neurons is the name given to nerve cells together with their processes . About 50% of all neurons in the brain are found within the cerebellum, although their size relative to the brain is 10%.
Functions of the cerebellum according to the lobes
- Keep your balance. This function corresponds to the flocculum-nodular lobe.
- It acts in the preservation of muscle tone. Function that corresponds to the anterior lobe.
- It intervenes and regulates automatic and voluntary movements. It also coordinates the skeletal muscles. This is a specific function of the posterior lobe.
Type of connection between the brain and the cerebellum
The cerebellum establishes different types of connection with the cerebellar trunk. This connection is made possible by cords called cerebellar pendulums. There are 3 types:
- Superior cerebellar pendulum. They are motor fibers that come from the central nuclei of the cerebellum to the brain stem.
- Middle cerebellar pendulum. They are the thickest of the three. They connect the pons with the neo-cerebellum.
- Inferior cerebellar pendulum. It relates the medulla oblongata and the spinal cord .
Division of the cerebellum according to its evolution
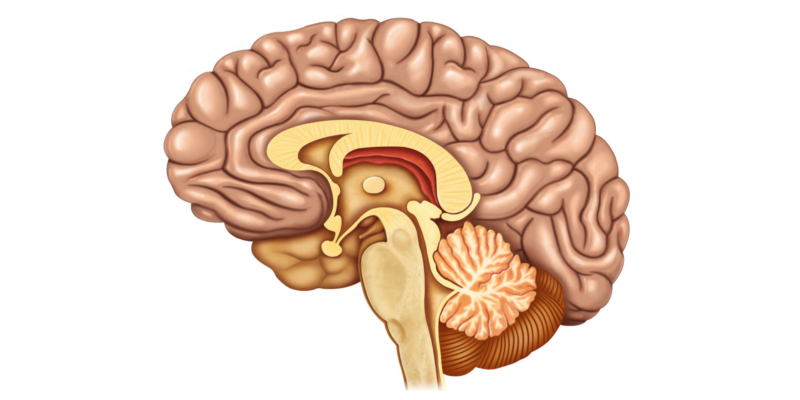
- Flocculum-nodular lobe. It corresponds to the most primitive part of the cerebellum.
- Anterior lobe. It is the second lobe in evolution.
- Posterior lobe. It is the most recent part in the evolution of the cerebellum.
Internal configuration of the cerebellum
It is divided into gray matter and white matter:
- Gray matter. It is made up of 4 cerebellar nuclei and the cortex. These 4 cores are:
- Fastigial nucleus. It has to do with the functions of balance.
- Globose nucleus. It is shaped like the letter "S".
- Emboliform nucleus. It is responsible for the movements of the limbs.
- Serrated nucleus. It is the most developed and is the one that connects with the neo-cerebellum.
- White matter. It is located in the middle part of the cerebellum. It comes in a branched form. For this reason it is called the tree of life .
Diseases and injuries of the cerebellum
- Cancer
- Genetic diseases, such as the Dandy Walker malformation.
- Cell degeneration. It is produced by faulty brain cells .
- Lower than normal muscle tone.
- Movement disorder (Ataxias). It is the lack of muscular control in the legs and arms.
Genetic rarity about the cerebellum
Given the functions described above, it would be impossible to believe that a human being could live without a cerebellum . However, there are people who, after relevant studies, are found to have been born without a cerebellum.
Although the lack of it at birth could suggest a premature death, there are currently 9 registered cases of adults without a cerebellum. This phenomenon of malformation and survival accounts for the adaptive plastic capacity of the human brain to the environment . However, it is still a rarity and a malformation with little chance of survival in general.
The above content published at Collaborative Research Group is for informational and educational purposes only and has been developed by referring reliable sources and recommendations from experts. We do not have any contact with official entities nor do we intend to replace the information that they emit.
MA student of the TransAtlantic Masters program at UNC-Chapel Hill. Political Science with a focus on European Studies. Expressed ideas are open to revision. He not only covers Technical articles but also has skills in the fields of SEO, graphics, web development and coding. .
Leave a reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Recent post

Sport: What Is It, Types, Risks, Features, Characteristics and Examples

Dogs: Emergence, Features, Characteristics, Feeding and Breeds

Story: Definition, Elements, Structure, Features and Characteristics

