We explain what earthquakes are and their causes and consequences. Also, what are its characteristics and classification.
What are earthquakes?
Earthquakes or tremors are called sudden and temporary shakes of the earth's crust due to the release of energy in the subsoil in the form of seismic waves, as a consequence of geological movements and displacements of the tectonic plates that make up the upper layers of the planet.Earthquakes are more or less unpredictable phenomena that occur on our planet from very early times, as evidenced by the different geological faults that gave rise to the relief : mountains , valleys, etc.
The surface of the Earth moves (although kilometers deep) and these movements, together with other similar phenomena such as volcanoes and even sometimes by human actions, produce vibrations that, when transmitted to the surface, generate a shake .
Earthquakes can be mild or intense , and they can go unnoticed (seismic movements occur daily without us noticing) or they can be remarkable and even, as in earthquakes, devastating for life as we know it.
What are the causes of an earthquake?
 Most earthquakes are the consequence of natural geological processes , such as the movement and collision between tectonic plates: the masses of the earth's crust that float in the magma inside the planet, and that move very slowly, generating friction with each other.
Most earthquakes are the consequence of natural geological processes , such as the movement and collision between tectonic plates: the masses of the earth's crust that float in the magma inside the planet, and that move very slowly, generating friction with each other.However, phenomena that affect atmospheric pressure, such as intense cyclones or changes in the rainfall regime , can cause microseisms, detectable only by seismographs.
At the same time, the human hand can cause earthquakes induced by different techniques for exploiting the earth's crust, such as catalytic fracking of oil , or the cooling of the crust by pouring cold water into geothermal reservoirs (in power generation plants). geothermal energy ).
Another possible case is the underground detonation of atomic bombs , although these cases really represent rather minor earthquake options.
What consequences do earthquakes have?
 Mild earthquakes are basically harmless, but larger ones can scare the hell out of you or even cause damage.
Mild earthquakes are basically harmless, but larger ones can scare the hell out of you or even cause damage.An intense and prolonged earthquake can collapse buildings, shake and destroy streets , and cause objects to collapse on us.
The great earthquakes in history have, in fact, devastated entire cities and left thousands dead , homes devastated and people injured.
What types of earthquakes exist?
 Earthquakes can be of three types, depending on their specific origin:
Earthquakes can be of three types, depending on their specific origin:
- tectonic earthquakes. Caused by the movements of the tectonic plates, within two subcategories: interplate earthquakes, product of friction in contact areas between two tectonic plates; and intraplate earthquakes, which occur far from tectonic plate boundaries.
- volcanic earthquakes. They accompany the eruptions of the volcanoes since they are caused by the fracture of the rocks that the boiling magma heats in its path. They are usually smaller than the tectonic ones.
- collapse earthquakes. They occur due to the mechanical movement of large rock masses, such as cave collapses, avalanches or other high-impact accidents on the earth's surface or in its interior layers.
How are earthquakes measured?
Earthquakes are measured based on a double scale, which registers intensity on the one hand and magnitude on the other. These scales are:
- Of intensity. They measure the strength of the tremor based on the damage caused. There are the Mercalli scale (12 points), the Medvédev-Sponheuer-Kárnik (12 points) and the Shindo scale (7 points).
- of magnitude. They measure the amount of tremor energy based on its reverberations. There is the Richter scale (7 points) and the seismological moment magnitude scale.
What is the difference between earthquake and earthquake?
 In principle, there is no difference between an earthquake and an earthquake: every earthquake is an earthquake . However, in practice, the most intense earthquakes are called earthquakes, which have consequences in the lives of people and represent a danger to human communities . Otherwise, there is hardly any talk of earthquake or tremor.
In principle, there is no difference between an earthquake and an earthquake: every earthquake is an earthquake . However, in practice, the most intense earthquakes are called earthquakes, which have consequences in the lives of people and represent a danger to human communities . Otherwise, there is hardly any talk of earthquake or tremor.
What are the seismic zones of the world?
 The zones of greatest seismic probability in the world are those, in general, in which the tectonic plates exert pressure on each other, called faults . Some of the best known are:
The zones of greatest seismic probability in the world are those, in general, in which the tectonic plates exert pressure on each other, called faults . Some of the best known are:
- Altyn Tagh fault. This faulting began nearly 40 million years ago, as the Indian continental plate moved north and pushed against the Eurasian plate. It measures more than 2,500 km and includes the Kansu Fault at its eastern end.
- San Andreas Fault. Located in a large depression between the North American plate and the Pacific plate, it is 287,000 km long and cuts through the states of California in the US and Baja California in Mexico .
- San Ramon Fault. Located in the east of Santiago, the capital city of Chile , on the South American continent , 5 km from the surface and along 25 km of length, in a north-south direction.
Can they be monitored in real time?
There are seismic monitors worldwide that keep a local and international record of recorded telluric movements. These institutions can be consulted on the Internet in real time on pages such as these:
- iris consortium
- Argentine National Seismic Prevention Institute
What to do in case of earthquake?
 The best way to avoid further damage in the event of an earthquake is to be prepared and prepared for it, which is why it is convenient to learn what to do during an earthquake:
The best way to avoid further damage in the event of an earthquake is to be prepared and prepared for it, which is why it is convenient to learn what to do during an earthquake:
- Do not run, push others, or panic.
- Put out cigarettes and other flammable objects, as the tremor may have broken gas pipes.
- Stay away from windows, balconies, lamps, light and electricity cables , and bulky shelves or furniture that could fall.
- Do not use elevators or stairs (the latter only when the shaking has stopped).
- Take shelter under a frame or next to a column.
- Hide under a sturdy piece of furniture or table that supports the weight of the ceiling or wall when it collapses.
- Keep children and disabled people safe.
- Abandon the building and look for pre-established points of refuge when the earthquake has stopped, bearing in mind that there may be immediate aftershocks.
What is seismology?
Seismology is the branch of geophysics that studies earthquakes and telluric or tectonic movements , applying all the scientific knowledge that is available to try to prevent or at least better understand earthquakes.
In this sense, it studies not only the telluric cycles of plate movement, but also diagnoses the possible impact that certain industries may have on the appearance of earthquakes, or the damage that buildings may receive in the event of one.
What is a seismograph?
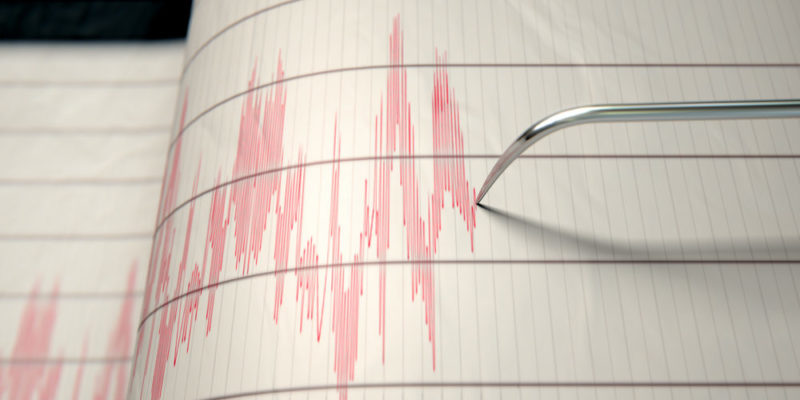 A seismograph or seismometer is an instrument invented in 1842 and refined over time , whose purpose is to measure the properties of seismic waves originating in the earth's subsoil, whether they are intense and notorious, or light and imperceptible.
A seismograph or seismometer is an instrument invented in 1842 and refined over time , whose purpose is to measure the properties of seismic waves originating in the earth's subsoil, whether they are intense and notorious, or light and imperceptible.With this type of apparatus , the seismic activity of the regions is recorded and tremors are measured, using the previously detailed scales.
The above content published at Collaborative Research Group is for informational and educational purposes only and has been developed by referring reliable sources and recommendations from technology experts. We do not have any contact with official entities nor do we intend to replace the information that they emit.
She has pursued her studies in The United States, where she has graduated in Business and Economics and is currently finishing her Master studies in International Economics and Finance. Miss. Amputee is fluent in three languages: English, Spanish and Russian and has elementary knowledge of French and Italian. She love exploring how Collaborative Research Group can become the best tool to achieve the (necessary) educational change. .
Leave a reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Recent post

Sport: What Is It, Types, Risks, Features, Characteristics and Examples
September 23, 2021

Dogs: Emergence, Features, Characteristics, Feeding and Breeds
September 24, 2021

Story: Definition, Elements, Structure, Features and Characteristics
September 24, 2021

Essay: Definition, Structure, Features, Characteristics, How to Do It
September 24, 2021
