We explain to you what was the evolution of the human being and what were its stages. Also, its general characteristics and different species.
What was the evolution of human?
The evolution of man or correctly said human evolution or evolution of the human being , was a slow process of change and adaptation that produced contemporary humans ( Homo sapiens ). It started from some ancestral species of ape-like primates.
It is a complex process that lasted approximately six million years . It encompasses the appearance and extinction of various species of the genus Homo , that is, not too distant relatives of our species, which preceded us in time. From them we inherit many of our biological properties.
Human evolution responds, like that of all known animal species , to the laws of speciation and other theories formulated from the scientific findings of Charles Darwin and its subsequent developers. In this sense, it is determined by genetic mutations and natural selection.
Origin of the human being
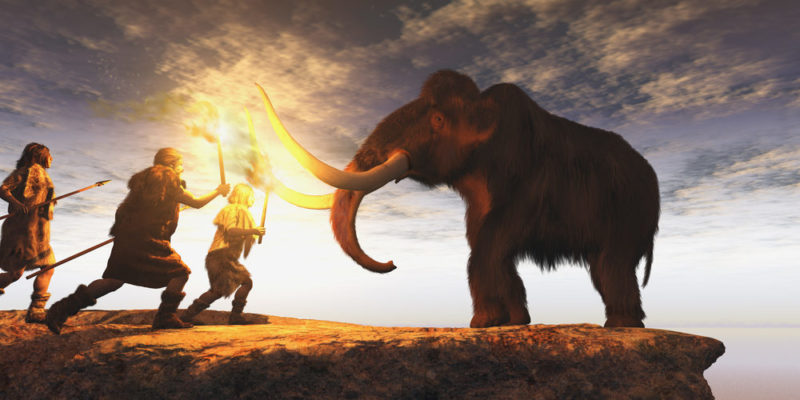

The first human beings, at least as we understand them today, belonging to the species Homo sapiens , emerged in Africa about 200,000 years ago.
The oldest archaeological remains that we have discovered of our species are in Kibish, Ethiopia, cradle of humanity .
There are many dating theories and attempts that place the first member of the species, the chromosomal Adam, around 90,000 years ago in sub-Saharan Africa.
From there, Homo sapiens would have migrated to the rest of the continents , rivaling other prehistoric human species and finally imposing itself as the dominant one on the entire planet .
Scientific evidence of the evolution of human
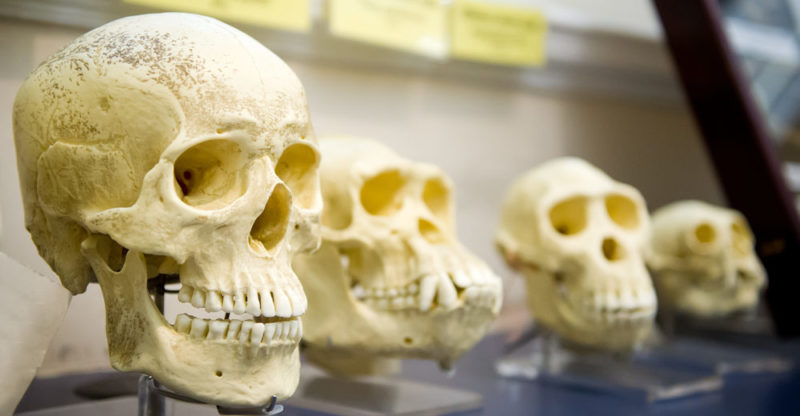
The study of the origin of our species has occupied our interest for centuries. Creationist theories inherited from our religious past have been developed , but also formulations that were scientifically proven.
To verify the scientific theories, biological , archaeological , anthropological and genetic reviews were carried out , among other sciences that have been dedicated to the study of the evolution of the human being. Numerous scientific evidences have emerged from these studies that affirm our kinship with other primates.
For example, we share a very high percentage of our genome with the chimpanzee ( Pan troglodytes ). In other words, the obvious physical and biological similarities, and even instinctive behavior, reflect a genetic closeness.
Stages of the evolution of human

Human evolution comprises the following stages:
- Emergence of Australopithecus. The beginning of our species occurred when a family of primates was forced to descend from the trees to look for alternative sources of food, either migrating to other less populated places or changing their diet based on what was found in the ground . Thus, they stood up on their hind limbs, acquiring an upright posture that allowed them to see their surroundings above the vegetation line, guaranteeing them more opportunities for survival in the plane. Thus arose the first australopithecines, completely bipedal apes.
- Beginning of the genus Homo . Australopithecines became extinct, but they gave way to new forms of life that henceforth belonged to the genus Homo , that is, they were Hominids . The first were Homo habilis and Homo rudolfensis , better prepared for life on the plane and able to use their upper limbs, now free, in the manufacture of stone tools with which to hunt and defend themselves.
- The time of migrations. Another species of hominin, called Homo erectus , descended from Homo habilis. Equipped with more complex tools, animal skins and possibly fire , they left the African continent to expand into the supercontinent Pangea, from which the five continents that we know would later emerge . The Homo erectus was the first human species to live gregarious, sharing resources, and perhaps it depended on immigration success, then giving way to new species.
- The emergence of new species. Spread throughout the world, the genus Homo began a process of speciation that produced various human species: Homo ergaster in Asia and Europe, from where Homo heidelbergensis emerged in Europe and later Homo neanderthalensis or Neanderthal man, one of the last species in exist, that coexisted with the first of ours. At the same time, the Homo antecessor emerged in Spain / Italy, the Homo floresiensis in Asia, the Denisova Hominid, among many others.
- Birth of Homo sapiens . While other species colonized the world, Homo sapiens or modern man emerged in Africa. It is precisely unknown which was the predecessor species of ours, but we know that about 90,000 years ago it expanded to the Middle East where it met Neardental Man, with whom it coexisted and even hybridized to a certain degree, before that the latter was extinguished and the sapiens finally conquer the entire planet.
Human brain development
One of the most outstanding features of the human evolutionary process has to do with the development of our most powerful weapon: the brain and its learning capacities. The evolutionary history of our brain would be something like this:
- Australopithecus . It has an average of 450 cm3of cranial capacity, little more than a chimpanzee.
- Homo habilis . Much more developed, around 650 cm 3 of brain.
- Homo erectus . Initially it showed about 850 cm3, but its last individuals could have reached 1100 cm3.
- Homo neanthentalensis. It reached just over 1150 cm 3 of cranial capacity.
- Homo sapiens . It has an average capacity of 1,350 cm3of brain.
Opposable thumbs
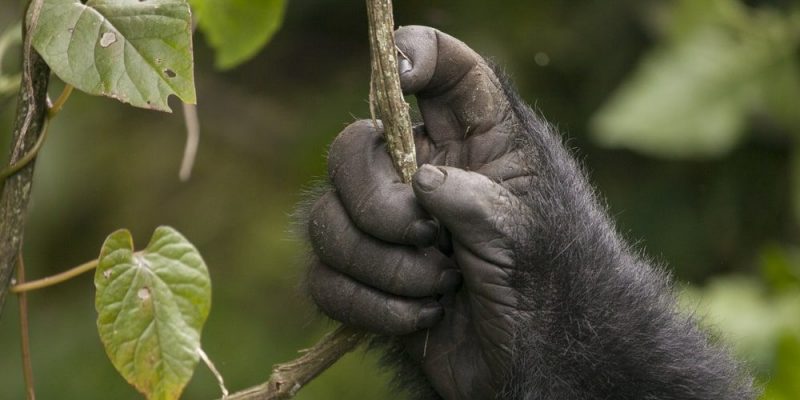

One of the particular features of human evolution is the presence and usefulness of opposable thumbs. We share this characteristic with the higher primates and it was only useful once the bipedal posture was developed and the upper extremities released.
Since our thumbs can touch the tips of the rest of the fingers , they allow us the precise, exact use of tools handled with our hands. Imagine that you did not have thumbs: could you use your everyday instruments?
Articulate language
One of the major features that distinguish Homo sapiens from its predecessors is the emergence of an articulate language , that is, symbolic. It allows us, among other things, to formulate and share complex thoughts , which refer to objects that are not present, but that we can exchange for signs.
There are suspicions of the presence of a very primitive language in H. erectus and more developed in H. nearthentalensis. However, none would have reached the complexity of ours.
Standing

Unlike the straight spine of apes, the spine of humans and their ancestors is curved . They are designed for a bipedal life, standing flat, because they allow them to support the entire weight of the body . Our spine works like a spring, with round vertebrae that support the weight of the head and torso.
The same happened with the pelvis, which had to widen and rotate towards the inside of the body . This allows the weight of the body to be supported but represents a difficulty for the birth of the young, since it provides the females with a long and sinuous birth canal. Therefore, they must be born prematurely and complete their process outside the mother's body.
Does the human descend from the ape?
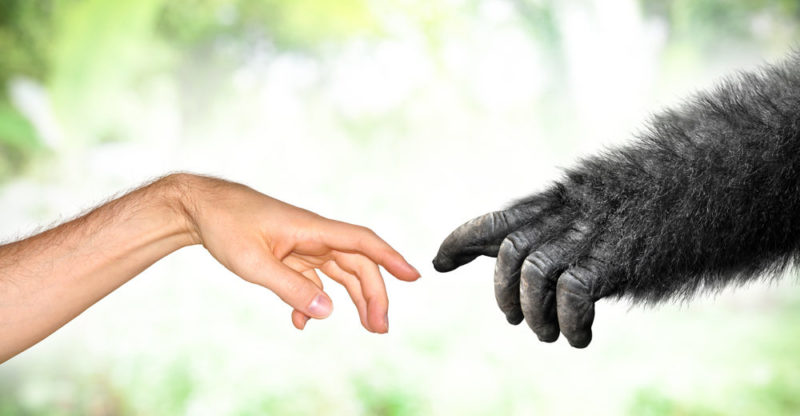

Contrary to what is popularly thought, evolutionary theory does not affirm that the human being descended from the monkey , that is, that we are a species of gifted monkeys that millions of years ago separated from the current monkeys.
In reality what this theory holds is that apes and humans come from a common prehistoric ancestor . That is, in the tree of known life we occupy the same branch, but we had different, separate evolutions. It is not that we come from them but that we are their distant relatives.
Future of human evolution
The evolutionary future of our species is uncertain, and many writers and thinkers have fantasized about what the remote future might hold for us as a species. Everything will depend on the environmental conditions in which we live .
For example, the expansion of the species to various planets of the solar system would diversify the conditions of life and eventually lead to the origin of new species of human, genetically and biologically different.
Timeline

An evolutionary timeline containing the main human species would be as follows:
- Australopithecus afarensis. It arose approximately 4 million years ago and became extinct 2.8 million years ago.
- Homo habilis . It arose 2.6 million years ago and became extinct 1.5 million years ago.
- Homo erectus . It arose 1.9 million years ago and became extinct approximately 400 thousand years ago.
- Homo nearthentalensis . It arose 500 thousand years ago and became extinct sometime thousands of years ago.
- Homo sapiens . It arose approximately 200 thousand years ago and it still exists today.
Anas is an editor of a prestigious publishing company in the United States. She studied Mathematics in Arizona. Anas is also a teacher and one of her long-term goals is to build an institution that offers free education to everyone who are financially not stable. .
Leave a reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Recent post

Sport: What Is It, Types, Risks, Features, Characteristics and Examples

Dogs: Emergence, Features, Characteristics, Feeding and Breeds

Story: Definition, Elements, Structure, Features and Characteristics

