We explain what the planets are, how they originated, and their classification. Also, what are its characteristics and its movements?
What are the planets?
Planets (from the Greek planëtes , which translates as "wanderer" or "wanderer") are called certain natural astronomical bodies, of relatively large size , that move on an orbit around a star (such as the Sun ).
Unlike stars, they lack their own light and energy emissions from nuclear reactions inside them.
In other words, planets are large, opaque bodies that orbit stars. In turn, they can be orbited by moons or other natural (and artificial) satellites, being the dominant object throughout their orbit.
Specialists impose other requirements on astronomical bodies that meet these basic conditions to distinguish them from asteroids and other space objects:
- Size. At least 1,000 kilometers in diameter.
- Shape. Spherical due to the effect of its own gravity .
- Mass. Not so massive that its gravity would produce atomic fusion reactions in its core.
How did the planets originate?
There is no consensus regarding the exact origin of the planets.
However, the most accepted theory is that they were part of the disk of gas and dust from which stars are formed , which by attracting heavy elements ends up becoming a planetesimal.
This first formation merges with others due to the effect of gravity until it forms a larger element.
The gravity of this larger object manages to capture gaseous elements in the form of an atmosphere around it.
Classification of the planets

The planets can be classified according to various criteria, such as their spatial location (within our Solar System , within some other or without any system), but above all according to their size.
Thus, we can talk about:
- Gas giants. Huge balls of fluid ( gas or liquid ) that often surround a rocky or metallic core. They lack a well-defined surface and are often composed of different proportions of hydrogen and methane. In some cases, when these planets are far from a stable energy source (such as a star), their fluids can freeze and they become icy giants.
- Terrestrial planets. Also called telluric or rocky planets, they are made up of silicate mantles that surround a metallic core, usually iron . They have a clearly defined surface, with canyons, craters, volcanoes or even large bodies of water, and a secondary atmosphere produced by their own internal processes.
- Tiny planets. This is a recent category (2006) and is actually used to distinguish between planets themselves and those objects that meet all the conditions to be so, except for dominance over their orbit, since they do not have enough mass. It is an intermediate category between planet and asteroid.
Planetary movements
The planets move along orbits , attracted by the gravity of their respective stars. This motion around the larger star is known as translation. In the case of our planet, the translation marks the course of the year.Not all the planets do it at the same speed , nor do they have orbits of the same size: the further away they are from their axis of translation, the longer and slower this movement is.
Since the Earth 's axis is tilted, there are sectors of the orbit where the southern hemisphere points more directly towards the Sun, and other sectors where the northern hemisphere is more exposed. This is due to the change of seasons.
On the other hand, the planets also rotate on their own axis , in what is known as rotational movement, and which can occur at different speeds. In the case of Earth this produces day and night and takes 24 hours to occur; but on other planets it can be much faster or much slower.
The solar system
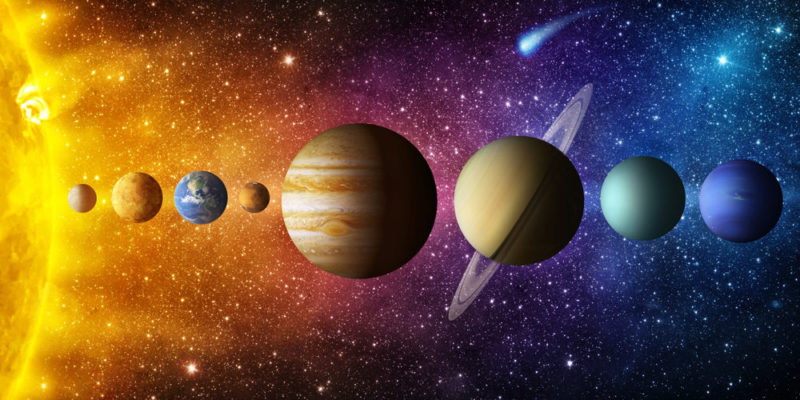 Our Solar System is the set of planets and astronomical objects that orbit the star at its center, the Sun.
Our Solar System is the set of planets and astronomical objects that orbit the star at its center, the Sun.So far we know that it is made up of eight main planets : four inner and four outer, each with their respective natural satellites . In addition, it includes two asteroid fields and four dwarf planets.
Inner planets
 The inner planets are those that are closest to the Sun , orbiting between this star and the asteroid belt .
The inner planets are those that are closest to the Sun , orbiting between this star and the asteroid belt .These planets have a similar size, a higher density and a clearly differentiated structure , with solid surfaces and atmospheres. The inner planets are Mercury , Venus , Earth, and Mars .
Outer planets
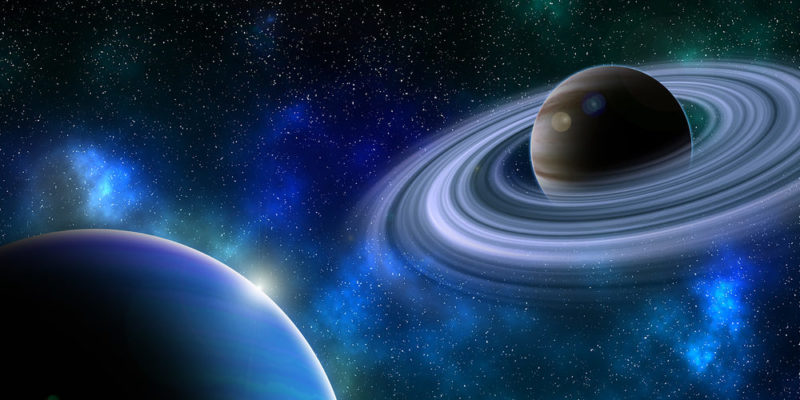 This is how the planets on the outer side of the asteroid belt are known , that is, those farthest from the Sun.
This is how the planets on the outer side of the asteroid belt are known , that is, those farthest from the Sun.They are gigantic and gaseous planets , with no defined surface, with very fast rotation periods and strong magnetic fields . In some cases, they have ring systems surrounding them.
The outer planets are Jupiter , Saturn , Uranus, and Neptune .
Tiny planets
 The concepts of planet and dwarf planet were redefined in 2006 .
The concepts of planet and dwarf planet were redefined in 2006 .The latter were defined as those celestial bodies whose masses are too small to prevail over their orbits and force other bodies to orbit around them as moons. But at the same time they are too big (and their very spherical and regular shapes) to think that they are asteroids.
The dwarf planets in the Solar System are Ceres, Pluto , Charon, and Eris .
To them could be added other planetoids often referred to as "Trans-Neptunian Objects" , being beyond the orbit of Neptune. Among them are Makemake, Orcus, Quaoar, Varuna, Ixion, and others.
Extrasolar planets
This is the name given to the planets that are not part of our Solar System , but of some other.It is very possible that each star in the universe has its own planetary system, but until 1992 it had not been possible to prove its existence. The vast majority of these planets are Jupiter-like gas giants .
Interstellar planets
 They are also called wandering planets or orphan planets. These are those that for one reason or another do not orbit any star , but have the rest of the conditions to be considered planets.
They are also called wandering planets or orphan planets. These are those that for one reason or another do not orbit any star , but have the rest of the conditions to be considered planets.Therefore, these planets move through space as independent objects, adrift.
habitable planets
Human beings have long dreamed of colonizing other planets . However, no other within the Solar System meets the minimum characteristics to sustain life as we know it, which makes the Earth a very special planet, with its large deposits of liquid water .However, in our search for a future new home, we have already identified 57 potentially habitable extrasolar planets , judging by their similarity to Earth. The closest of them is 305.09 light-years away.
The above content published at Collaborative Research Group is for informational and educational purposes only and has been developed by referring to reliable sources and recommendations from technology experts. We do not have any contact with official entities nor do we intend to replace the information that they emit.
Luke is passionate about fostering student involvement and connection. He studied psychology for his major and likes learning about the past. Luke aims to specialize in artificial intelligence and cybersecurity. .
Leave a reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Recent post

Sport: What Is It, Types, Risks, Features, Characteristics and Examples

Dogs: Emergence, Features, Characteristics, Feeding and Breeds

Story: Definition, Elements, Structure, Features and Characteristics

