We explain what the postclassic period is, its historical context and its characteristics. Also, what are the main civilizations and more.
What is the postclassic period?
The Postclassic period corresponds to the last stage of the history of pre-Columbian America, between 900 AD. C. and 1521 d. C. This stage was marked by the decline of the great civilizations that inhabited Mesoamerica , in a context of large military deployment, economic problems and populations very numerous.
Among the main cultures of the Postclassic period , the Mayan, Inca and Aztec empires stood out, whose history was interpreted based on archaeological evidence and the chronicles of the Spanish who colonized the American lands and defeated the peoples.
Historic context
The term “Mesoamerica”, which comes from the Greek, means intermediate America and refers to the territories of Mexico , Guatemala , El Salvador, Belize, Nicaragua , Honduras and Costa Rica.
The Mesoamerican Postclassic period included the end of the Middle Ages (from 400 AD to 1492 AD) and began the Modern Age with the European invasions of America .
The Mayan civilization , made up of a group of independent city-states, managed to be the most powerful and advanced of the classical period, which was characterized by the constant increase in populations, imposing buildings and advanced agricultural techniques that allowed economic progress.
Characteristics of the Postclassic period
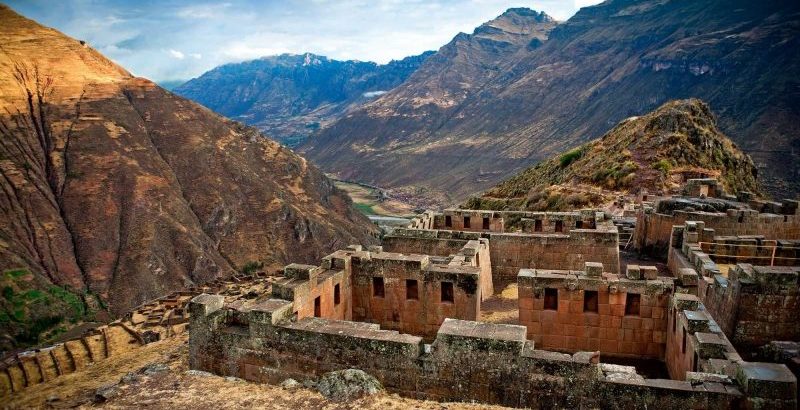

The Postclassic period was characterized by two main stages:
- Early Postclassic (900 - 1200 AD). It stood out for the decline of the cities that had reached their splendor during the Classic period , especially the Mayan civilization and its alliances. Some hypotheses maintain that, in addition to the military interventions, the collapse could be due to severe droughts , a consequence of climatic changes that affected the use of the soil for crops.
- Late Postclassic (1200-1521 AD). It stood out for the large extension of built-up territories that had been abandoned by the ancient sedentary peoples, as a result of internal conflicts between independent states and the European military invasions from 1492. The regions of the highlands of Guatemala evidenced a significant increase in the population, especially of the indigenous Quiché and Cakchiquel peoples.
Postclassic economics
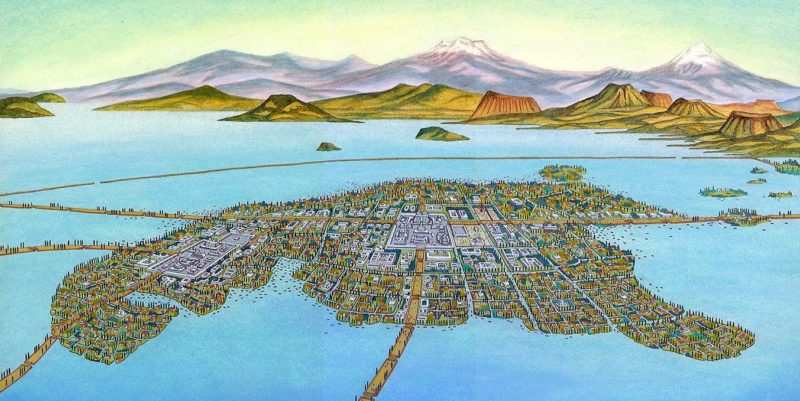 The Postclassic economy was based on agriculture as the main livelihood, which was also an activity influenced by religious beliefs. Its inhabitants believed that the fertility of the land and the productivity of crops depended on the influence of the gods.
The Postclassic economy was based on agriculture as the main livelihood, which was also an activity influenced by religious beliefs. Its inhabitants believed that the fertility of the land and the productivity of crops depended on the influence of the gods.They made sophisticated hydraulic systems for irrigation , as in the important city of Tenochtitlán, in Mexico. It consisted of an island surrounded by canal systems and fields. All these advances in agriculture made it possible to achieve greater production that contributed to the development of trade with neighboring populations.
Major Postclassic civilizations
Among the main civilizations of the Postclassic period, the following stood out:
- Mayans . They were one of the most advanced civilizations in pre-Columbian Mexico, with a complex and sophisticated culture. The social organization consisted of different independent cities under the rule of an elite military and priests. The Mayans created a number system and were able to perform complex astronomical calculations.
- Aztecs . They were a militaristic state under the rule of a rigorous semi-divine ruler, along with the military and priests. The society was made up of artisans, merchants, peasants, and slaves. The Aztecs developed an unprecedented educational system, due to advances in writing and mathematics .
- Incas . They formed the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The government was of the monarchical and theocratic type, in charge of "the Inca", together with the priests and the armed forces. They had an exemplary and organized administration, with great control of population, tax, and resource records. The society was made up of artisans, peasants, and slaves.
Pre -Columbian cultures of the Postclassic period achieved sophisticated knowledge of astronomy, mathematics, agricultural techniques, metalworking (such as gold , silver, and copper ), and writing . They created highly precise calendars and built imposing urban architectural centers, such as Tenochtilán, in present-day Mexico City .
The european invasion
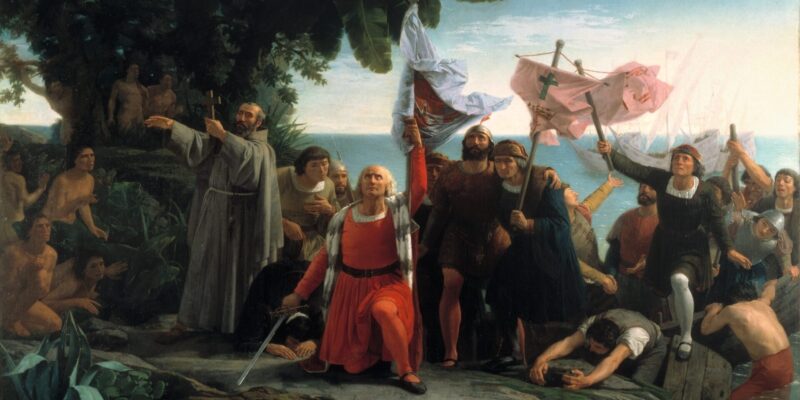

The European invasion of America began with the arrival of the Spanish in 1492 , at which time they found a continent inhabited by different civilizations, among the most important, the Mayas, Incas and Aztecs. The Spanish established the first European colony on the current island divided into two countries, Haiti and the Dominican Republic.
The end of the Middle Ages was established. From 1500 the Modern Age developed as a consequence of the meeting of the old world, made up of Europe , Asia and Africa , and the new world, made up of America.
Between 1519 and 1521 the Europeans returned to the American continent with the aim of dominating the Mesoamerican civilizations and carried out the most significant conquests, in principle, of the civilizations located in the territories of Mexico. Through force , economic exploitation, the usurpation of resources and the Christianization of the Indians, they devastated Mesoamerican cultures.
The above content published at Collaborative Research Group is for informational and educational purposes only and has been developed by referring reliable sources and recommendations from technology experts. We do not have any contact with official entities nor do we intend to replace the information that they emit.
Luke is passionate about fostering student involvement and connection. He studied psychology for his major and likes learning about the past. Luke aims to specialize in artificial intelligence and cybersecurity. .
Leave a reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Recent post

Sport: What Is It, Types, Risks, Features, Characteristics and Examples

Dogs: Emergence, Features, Characteristics, Feeding and Breeds

Story: Definition, Elements, Structure, Features and Characteristics

