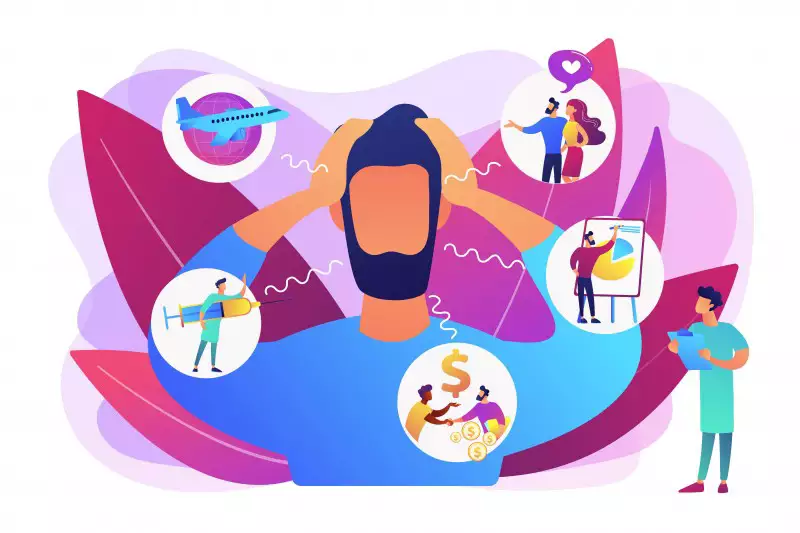
Anxiety is a general term for various disorders that cause nervousness, fear, apprehension and worry.
Anxiety is a reaction that every individual experiences in the face of some everyday situations, such as public speaking, anticipation of important dates, job interviews, the eve of tests, health exams, among others.
However, some people experience this reaction more frequently and intensely, which can be considered pathological and compromise emotional health.
How do you know when normal anxiety crosses the line and can be considered a disorder ? Check out more in the text below.
Anxiety and Fear
According to the DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders) anxiety disorders include those that share characteristics of excessive fear and anxiety and related behavioral disturbances.
Thus, fear is the emotional response to real or perceived imminent threat, while anxiety is the anticipation of future threat.
Fear is most often associated with periods of heightened arousal needed for fight or flight, thoughts of immediate danger, and behaviors aimed at escaping a situation.
Panic attacks stand out among anxiety disorders as a particular type of fear response.
How to control anxiety?
We learn to control anxiety when we discover its emotional triggers . Thus, one of the best current tools to deal with anxious moments is psychotherapy.
It is possible to identify triggers on your own or with the therapist. Sometimes the paths are obvious, such as excessive consumption of caffeine, alcohol or cigarettes . Other times they may be less obvious.
Eventually, long-term problems such as financial or work-related difficulties may take some time to be discovered.
Thus, we can be impacted by a due date, a person or the situation and not realize it. This may require some extra support, through therapy , or with friends and mentors.
When you discover your trigger or triggers, try to limit your exposure if you can. However, if you cannot or cannot reduce contact, as in the case of a stressful work environment that cannot be changed at the moment, using other coping techniques can help.
What characterizes anxiety disorder?
Anxiety disorders are distinguished from normal, adaptive fear or anxiety by being excessive or persisting beyond developmentally appropriate periods.
Thus, they differ from transient, often stress-induced fear or anxiety by being persistent.
What are the Symptoms of Anxiety ?
See what are the main symptoms that may be related to anxiety disorders, and deserve attention:
- See danger in everything;
- Deregulated appetite;
- Sleep changes;
- Muscle tension;
- Fear of public speaking;
- Excessive worries;
- Always being close to nervous breakdowns;
- irrational fears;
- Constant restlessness;
- Physical symptoms;
- Obsessive thoughts;
- Perfectionism;
- Digestive problems.
1 – See danger in everything
Individuals with anxiety disorders often overestimate the danger in situations they fear or avoid. Likewise, fear or anxiety is excessive or out of proportion.Have you ever met someone who doesn't travel by plane because they are afraid of a plane crash? Are you always thinking that the plane is going to crash? Can you even imagine the mourning scene ?
Another example is someone who undergoes a simple medical procedure or test and fears that he or she will have a serious illness or be disabled after the test. In more extreme cases, he even considers the possibility of dying during the procedure.
2 – Dysregulated appetite
There are many cases of people who find a solution to their emotional problems in food. That is, at the slightest sign of concern, you turn to the brigadier, a sweetie or any other food to relieve tension.In general, they chew food little and eat a large amount of food in a short time.
Eating indiscriminately, without hunger, due to anxiety, stress or another negative emotion is a warning sign. And watch out! This attitude can also trigger an eating compulsion .
3 – Sleep changes
Have difficulty sleeping or experience episodes of insomnia on the eve of important meetings and events. They can't disconnect from what they've done throughout the day at work and spend the night processing what they'll do the next day.Sometimes they even dream and wake up thinking about possible solutions to a certain issue.
4 – Muscle tension
It is common to suffer from pain in the back, shoulders and neck. Neck muscles are locked and the pain is so much that you can barely turn sideways.This almost constant muscle tension often accompanies anxiety disorders. The greater the concern and discouragement, the greater the possibility of transferring tensions to the cervical region.
5 – Fear of public speaking
Just thinking about the need to make a presentation to an audience do signs such as excessive sweating, icy hands, tachycardia, shortness of breath and wheezing appear.This fear may be related to ego concerns , fear of judgment and apprehension, which increases anxiety.
6 – Excessive worries
They are always worried about the future. Even more so in times of economic crisis, it is common to see people thinking about keeping their jobs.Excessive worry is a direct source of headaches, ulcers, anxiety and stress, and can even affect the immune system.
In addition, this anguish and the volume of details to think about greatly affects the attention of the person with anxiety, which makes it difficult to focus.
Thus, she loses efficiency in her daily activities, and this increases her concerns, making everything a cycle that can lead to despair and other problems.
7 – Always being close to a nervous breakdown
People who are on the verge of a nervous breakdown can quickly go from euphoria to tears. Symptoms such as irritability and sudden mood swings , with no apparent explanation, arise in times of greater pressure and stress.
8 – Irrational fears
Fears of missing something, of not being good enough, fear of failure, panic of being alone or not being accepted also haunt anxious people.Self-criticism champions are the first to not feel capable enough to complete a certain activity. Excess fear can compromise security in personal relationships, whether at work or in the family.
9 – Constant restlessness
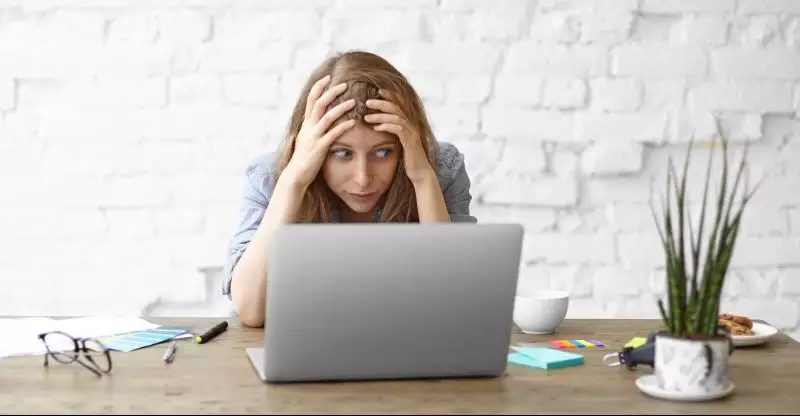

Factors that generate great discomfort by hindering the completion of a task, in addition to affecting the quality of life of the person himself and also of those who are beside him.
10 – Physical signs
In times of anxiety, physical symptoms may arise that go beyond muscle pain:
- tremors;
- tiredness
- feeling short of breath or choking;
- accelerated heart;
- excessive sweat;
- cold, sweaty hands;
- dry mouth, dizziness;
- nausea;
- diarrhea;
- abdominal discomfort;
- hot flashes;
- chills;
- frequent urination;
- difficulty swallowing;
- choking sensation.
11 – Obsessive thoughts
Obsessive thinking is an inability to gain control over recurrent, distressing thoughts and images. Brain imaging studies indicate that it is associated with a neurological dysfunction of unknown cause that forces thoughts into repetitive cycles.As such, obsessive thinking may also be associated with mood disorders, including dysthymia , depression , and bipolar disorder . It is also the defining symptom of Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD), Panic Disorder and many other psychological conditions.
12 – Perfectionism
Perfectionism is characterized by the insistence on setting high standards and the relentless pursuit of achieving them.Indeed, perfectionists are often high performers – but the price of that success can be chronic unhappiness and dissatisfaction. Excessive perfectionism can be strongly linked to fear of making mistakes and self-sabotaging behaviors such as procrastination .
Thus, as perfection is practically impossible to achieve, perfectionist people end up suffering from anxiety for not being able to reach the established goal.
13 – Digestive problems
A system greatly affected by stress and anxiety is the gastrointestinal tract . . Pain, poor digestion, discomfort in the abdomen, diarrhea and heartburn are some of the signs.Consequently, excessive anxiety and acute stress can alter gastrointestinal functions via the nervous system.
As a result of these changes, ulcers, gastritis, inflammatory diseases, gastroesophageal reflux and irritable bowel syndrome may arise.
Also Read: Stages of Grief: Know your stages and how to deal with the loss
Strategies to manage anxiety
Controlling anxiety is a challenge, but there are strategies, resources and even changes you can make in your everyday life that will help with this!We've listed a few below. Look:
Psychotherapy Sessions
Psychotherapy is a process that can help, and a lot, individuals suffering from anxiety. It is a collaborative treatment based on the relationship between an individual and a psychologist.Dialogue-based, it provides a supportive environment that allows you to speak candidly with someone who is objective, neutral, and nonjudgmental.
You and your psychologist will work together to identify and change the thought and behavior patterns that keep you from feeling your best, increasing self-awareness and resilience .
One of the most efficient approaches in the treatment of anxiety conditions is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, which has a very focused and direct performance.
Practice physical activity
Make time for a walk, run or any physical activity that gives you pleasure.Regular physical activity helps strengthen the immune system, prevent cardiovascular disease and obesity. . Likewise, it increases well-being, disposition for day-to-day activities and productivity at work.
It also decreases insomnia and improves mental health, preventing depression. However, if you're the competitive type, set a goal, such as running a 5K or 10K race.
As a result, the frequent practice of physical activity regulates sleep, as the practice of exercises releases endorphins, which provide well-being and reduce anxiety and stress.
Practice meditation
Neuroscientists have already proven that the practice of meditation helps to increase the region of the left prefrontal cortex, the region responsible for the feeling of happiness .Thus, five minutes a day to observe the breath is already efficient for the beginning. If possible encourage your team to meditate too, the gains will be huge.
Mindfulness is one of the most effective interventions to reduce stress and the immune system. I really like and use Headspace.
Listen to music
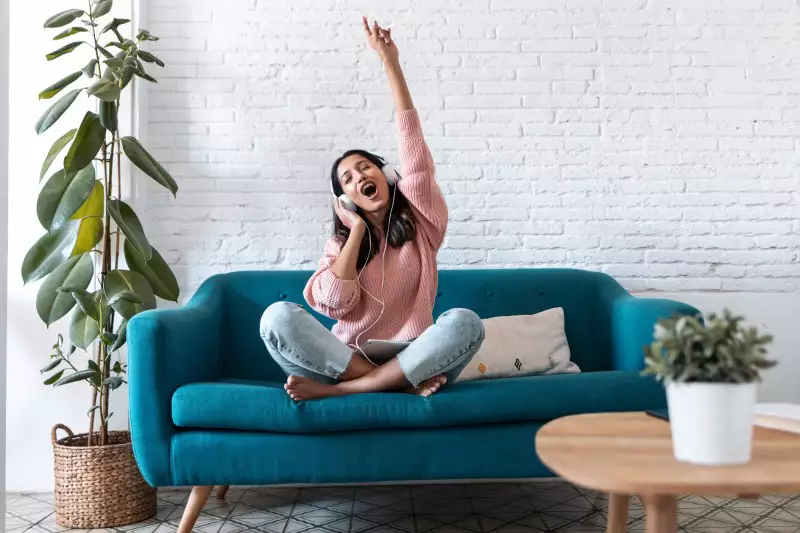

It is a therapeutic element par excellence. It is something medicinal and without contraindications. When was the last time you heard your favorite song?
Maintain a healthy diet
A healthy brain is the first line of defense against anxiety, depression and other mood disorders.Indeed, some vitamins are necessary for the formation of neurotransmitters that stimulate good mood , while others provide energy for brain cells or protect them from damage. Just like our organs, our brain needs certain vitamins to function normally.
We all go through moments of anxiety and stress. If they are very frequent or very intense, they may indicate the need for help from specialized professionals.
Leave a reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Recent post

Moral Values: What is it, definition and concept